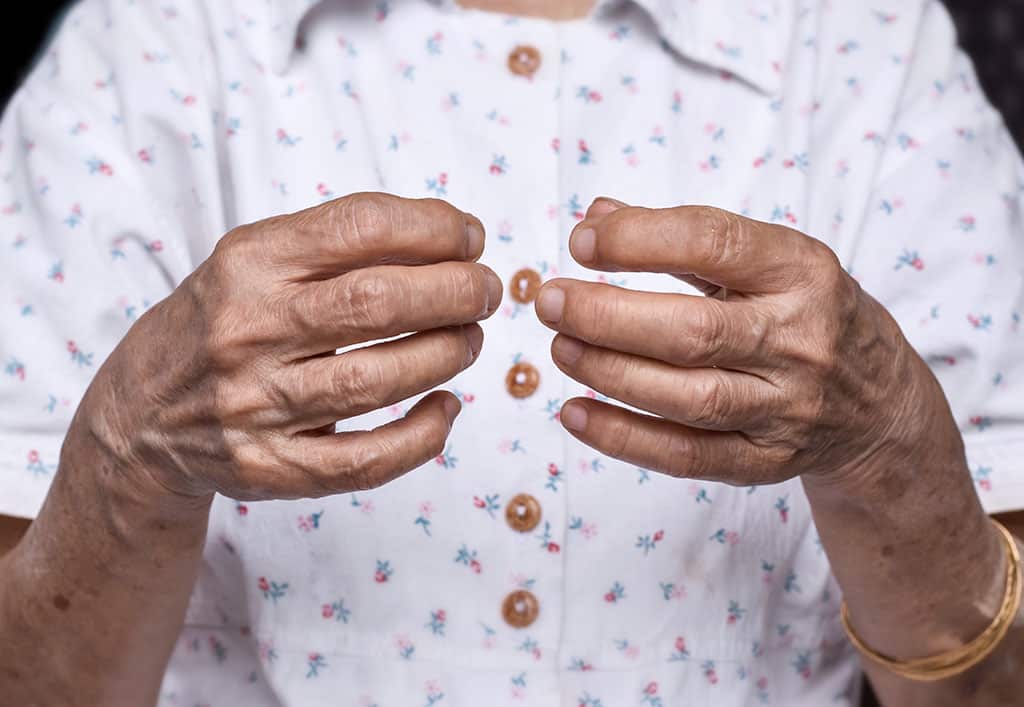
 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects more than 50 million Americans. In some of those cases, the disease is debilitating, making it difficult or impossible to perform routine, everyday tasks. RA is an inflammatory autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system starts attacking healthy cells, causing painful, stiff and swollen joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects more than 50 million Americans. In some of those cases, the disease is debilitating, making it difficult or impossible to perform routine, everyday tasks. RA is an inflammatory autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system starts attacking healthy cells, causing painful, stiff and swollen joints.
While RA can affect joints throughout your body, in most patients, it targets the joints located in the hands and feet first. The resulting inflammation, if left unchecked, can cause extensive damage to multiple systems in your body, even affecting the lungs, eyes and heart.
What Are the Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The sooner you recognize the early indicators of RA, the better your outcome will be. This is vital to ensure that we can offer timely management and symptom treatment.
Common early signs include:
- Persistent joint pain and stiffness: Typically of the small joints such as hands, wrists, feet or ankles. The pain and stiffness are often worse after inactivity and in the morning.
- Swelling: If you notice joint swelling accompanied by pain and stiffness, it is a sign of joint inflammation.
- Joint weakness: Weakness in the affected joints and the muscles surrounding it.
- Limited Range of Motion: As RA progresses, it’s more difficult to move your joints, reducing their range of motion.
At What Age Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Usually Start?
RA can occur at any time at any age. However, it’s most commonly found in those between the ages of 40 and 60. In addition, women are two to three times more likely to develop it than men. While it can occur in children and senior adults, this is uncommon.
What Could Trigger Rheumatoid Arthritis?
RA is a complicated disease, and there are several possible triggers that could cause a flare up. Research is still ongoing as scientists examine all the elements that are involved in developing the disease.>
However, a few factors that are triggers include:
- Genetics: If someone in your family has RA, you’re more likely to develop the disease.
- Age: As mentioned earlier, while anyone can develop the disease, most who have it are middle-aged, between 40 and 60.
- Sex: Women are more likely to develop RA than men.
- Smoking: Not only can smoking increase your risk, it can make the disease worse in those with RA or make the medications less effective. In addition, if you’ve been exposed to secondhand smoke, particularly as a child, you’re more likely to develop RA.
- No child: If you don’t have kids, studies show you might be at greater risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
- Being overweight or obese: The more overweight you are, the more likely you are to develop RA. This is based on your BMI or body mass index over 30. Not sure of your BMI? Use this useful BMI calculator to get your answer.
- Environmental exposure: If you’ve been exposed to harmful chemicals or toxins during your life, these can increase your risk or trigger RA.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Changes in hormones can affect the progression of RA. This is particularly evident in women.
What Diseases Can Mimic RA?
There are several diseases that can show similar symptoms to rheumatoid arthritis, which is why you need expert diagnosis and care from our rheumatologist in Raleigh. Many illnesses can present with joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Some of the diseases that can be mistaken for RA include:
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Lupus
- Palindromic rheumatism
- Viral arthritis
- Reactive arthritis
- Arthritis of IBD
- Lyme arthritis
What Is a Good Diet if You Have RA?
If you have RA, you’ll want to have foods that are rich in antioxidants, including dark leafy vegetables. Avoid fried food and beware of “add-ons” such as mayonnaise or excessive cheese. These foods can make you more vulnerable to inflammation.
In certain cases, elements of the Mediterranean diet can help you manage “flare-ups.” However, it’s important to realize that certain foods may trigger inflammation in certain people. Therefore, there is no “one size fits all” approach.
What Is the Most Effective Medication for Rheumatoid Arthritis?
First, we believe in treating the individualized patient. Therefore, we tailor our approaches to find the one that is best for you. This means that there is no one medication that will be appropriate for all types and forms of RA. In certain cases, a combination of therapies may be more effective. We will evaluate your situation and determine the best course.
However, in general, there are several various RA treatments that can minimize symptoms or keep them from getting worse. We’ll explore those treatments below.
These treatments include:
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
These work by modifying the immune response so that it does not attack healthy cells. They can also target molecules that are involved in the inflammatory process. It may take weeks or months before the full effect of DMARDs can provide relief.
DMARDs include:
- Methotrexate
- Hydroxychloroquine
- Sulfasalazine
- Leflunomide
Biologic Modifiers
These medications work by targeting the protein that sends inflammation signals to your body. Some of these include:
- TNF inhibitors (Humira, Enbrel, Remicade, Avsola)
- Interleukin-6 inhibitors (Actemra, Kevzara)
- Rituximab (Rituxan, Ruxience)
- Abatacept (Orencia)
Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors
These medications block certain enzymes that are a part of the immune response. As a result, they block or reduce RA inflammation.
Medications in this class include:
- Tofacitinib (Xeljanz)
- Baricitinib (Olumiant)
- Upadacitinib (Rinvoq)
Corticosteroids
These medications are typically used temporarily to give quick relief from RA pain and inflammation. Because these can cause patients to develop long-term side effects, these medicines are typically used for a short amount of time.
They include:
- Prednisone
- Prednisolone
NSAIDs
While these medications don’t slow RA progression, they do help manage inflammation and the pain associated with RA. You can get these over the counter.
Medicines include:
- Naproxen (Aleve)
- Meloxicam (Mobic)
- Celecoxib (Celebrex)
What Is the Normal Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
It may start subtly, with patients only experiencing slight pain and stiffness early in the morning.
If You Have Signs and Symptoms of RA, Schedule an Appointment With Us
If you have RA, then timely treatment is of the essence. It’s necessary to avoid some of the more serious complications that can accompany RA.
Dr. Priyank Chaudhary, a leading rheumatologist in Raleigh, will guide you through the latest treatments, evaluate your symptoms, and provide a carefully tailored plan to help you get your life back from the debilitating symptoms of RA.
Schedule an appointment to get started on your journey to wellness, where we can help you control and minimize the pain associated with RA. Getting started is simple: just ask your primary care provider to complete this basic referral form.


